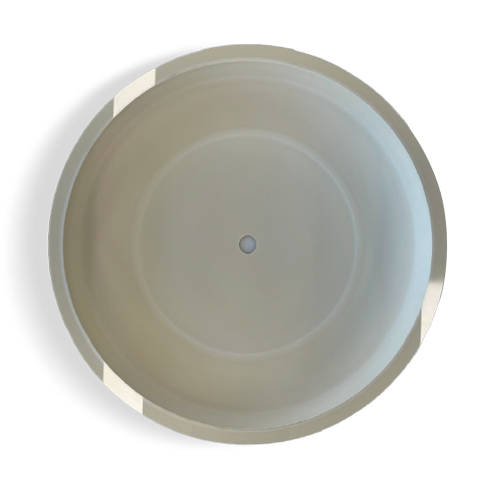
Alumina Ceramic
KCM Technology
Ceramic for Semiconductor Equipment
Dry equipment for semiconductor manufacturing processes, such as CVD, ALD, sputtering, and dry etch, operates in high-temperature and high-pressure environments during processing. Therefore, the components that make up the chamber must withstand the physical limits. Typically, the components used inside the chamber are made of ceramic materials that exhibit excellent resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, and chemical reactions.
Alumina ceramic, known for its heat resistance, wear resistance, plasma resistance, and electrical insulation properties, is utilized as a housing material to protect the entire chamber. It serves as the basic material for key components within the chamber, including the arm transporting wafers, upper electrodes (diffusers), lower electrodes (susceptors), and core components such as the photo chuck in the chamber.
- 99.99% Ultra-Pure Al2O3 Ceramic
- 99.8% Al2O3 Ceramic

99.99% Ultra-Pure Al2O3 Ceramic
Due to the continuous advancement in the semiconductor industry, there is a global surge in demand for ceramic materials suitable for long-term use in extreme (high power/high temperature) environments for semiconductor equipment and components.
The 99.99% ultra-pure Al2O3 ceramic is utilized for semiconductor equipment components primarily due to its strong resistance to plasma and excellent durability, making it suitable for high-power processes. As a result, the use applications are diverse in various areas within the electronics industry, including as materials for ESC (Electrostatic Chuck) components, microwave induction parts, chamber components, and insulating parts.
99.8% Al2O3 Ceramic
High purity Al2O3 ceramic materials with a purity of 99.8% or higher exhibit high resistance to chemical corrosion compared to other materials such as metals and plastics. They possess dense and high-hardness properties, offering excellent wear resistance.
Additionally, these ceramics demonstrate high electrical insulation at elevated temperatures and can withstand heat up to 1,600-1,700¡ÆC. Such characteristics allow the ceramic to become a core material for consumable parts used in processes like etching equipment, especially in environments requiring high-temperature vacuum plasma.
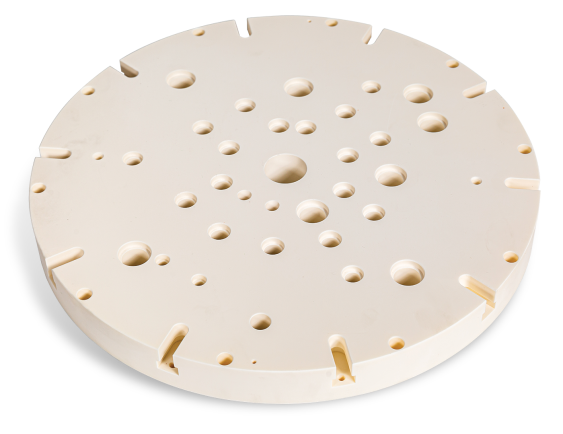

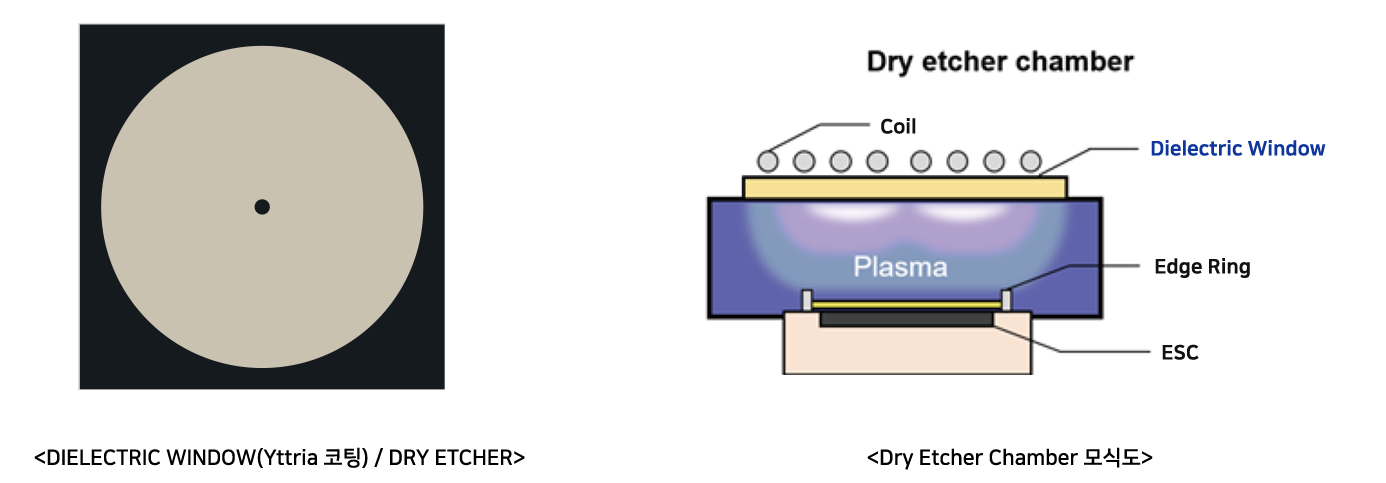
The DIELECTRIC WINDOW is a component of Dry Etchers, which are semiconductor processing equipment. It is utilized as the cover for the Etcher Chamber, as described above.
On the upper part of the DIELECTRIC WINDOW, a coil is installed to generate a fluorine-based corrosive gas plasma. The lower part is exposed to a high-density and powerful fluorine-based plasma, leading to erosion caused by exposure.
To improve process defects caused by particles and protect DIELECTRIC WINDOW products, a coating process is implemented for plasma resistance.
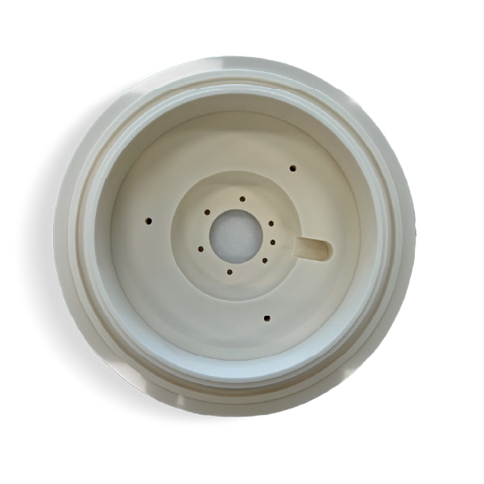

BASE CATHODE INSULATOR DPS MEC 99.8%
Al2O3 CERAMIC / DRY ETCHER
ULTIMA HDP CERAMIC DOME / CVD